A. The Arctic Circle (≈ 66½° N latitude) passes through 8 countries.
Countries (West → East):
- Norway
- Sweden
- Finland
- Russia
- United States (Alaska)
- Canada
- Denmark (via Greenland)
- Iceland
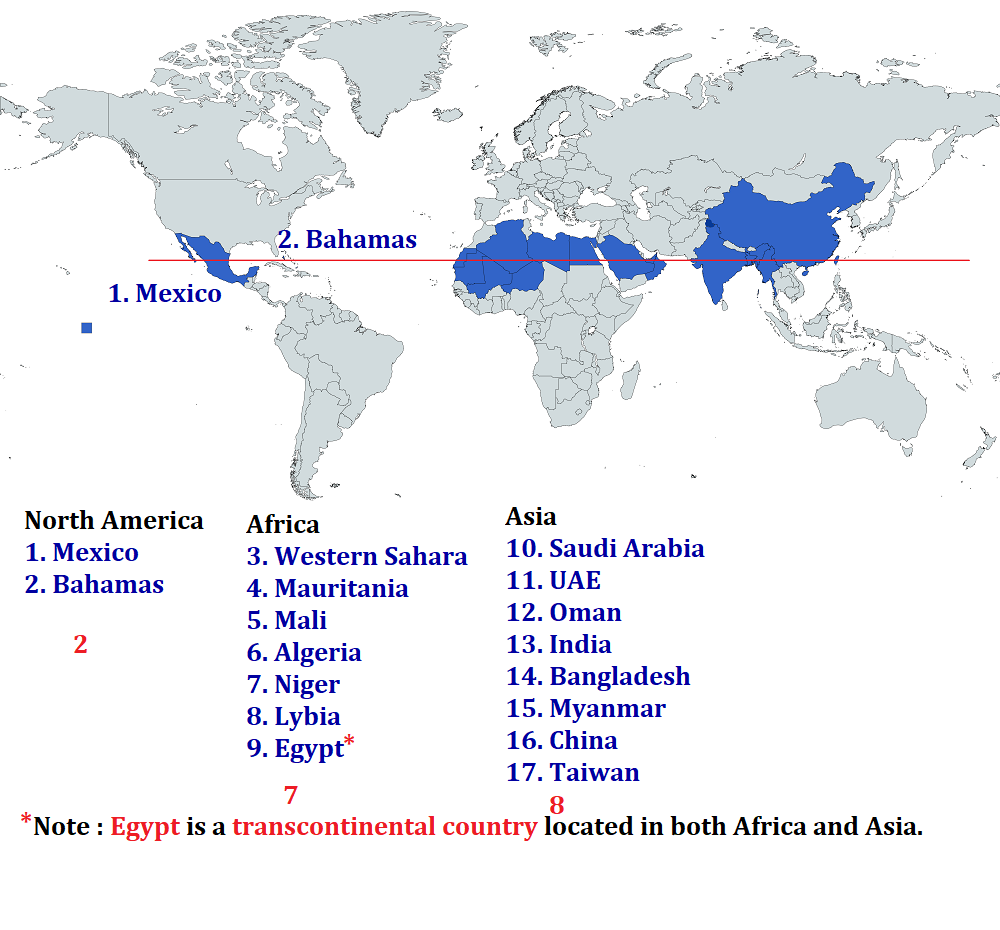
B. The Tropic of cancer passes through 17 countries, 3 continents and 6 water bodies.
Note : Egypt is a transcontinental country located in both Africa and Asia.
SOIL CHARACTERISTICS
- Entisols are immature soils lacking vertical development of horizons.
- Ultisols are associated with humid temperate to tropical climates.
- Mollisols are commonly found in grassland regions.
- Inceptisols are young soils more developed than Entisols.
IMPORTANT REGIONS
- Sahel region lies in North Africa.
- Kherson lies near the Black Sea.
- Batken lies in Kyrgyzstan.
- Paracel Islands lie in the South China Sea.
HUMAN GEOGRAPHY
- Pygmies are found in Equatorial Africa.
VEGETATION
🪨 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
- Sedimentary rocks are formed by lithification through consolidation and compaction of sediments.
- Sandstone and shale are examples of sedimentary rocks.
- Sediments result from weathering and erosion of all types of rocks.
- Sedimentary rocks are fossiliferous and contain fossils of plants and animals.
- Till is an ice-deposited sediment.
- Loess is a wind-deposited sediment.
SOIL TYPES
- Red soil is formed due to weathering of metamorphic and igneous rocks. [ Trick : Red coloured = MI Phone ]
🪨 DEGREE OF WEATHERING (ORDER)
- Granite → Basalt → Dunite → Rhyolite. [ Trick : Great Baadshah of Delhi was Rohillas ]
IGNEOUS ROCKS
- Igneous rocks are formed from magma or lava through volcanic activity.
- Coal is a sedimentary rock.
- Granite is an igneous rock.
🪨 METAMORPHIC ROCKS
- Gneiss, slate, marble, schist, and quartzite are metamorphic rocks.
🌍 EARTH’S INTERIOR
- Asthenosphere is the main source of magma.
- Barysphere refers to the Earth’s core or sometimes the entire interior.
TYPES OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
- Extrusive igneous rocks form when magma cools on the Earth’s surface.
- Intrusive (plutonic) igneous rocks form when magma cools at depth.
DEMOGRAPHY
- General Fertility Rate is the number of live births among women aged 15–44 years.
RENEWABLE ENERGY
- India’s first wind power project was established on 10 April 1999 at Amarsagar in Jaisalmer district, Rajasthan.
POPULATION
- Chandigarh, Uttarakhand, and Assam have population growth nearly equal to India’s average growth of about 17%.
INDIAN SOILS
- Alluvial soil is not found in Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim.
AGRICULTURE
- India is the world’s largest producer of jute.
- West Bengal alone accounts for about 70% of India’s jute production.
PHYSIOGRAPHY
- Jindhagada Peak is the highest peak of the Eastern Ghats.
INTERCONTINENTAL STATES
- Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Turkey are intercontinental countries.
GRASSLANDS
- Tropical grasslands include Savanna (East Africa), Campos (Brazil), and Llanos (Venezuela).
- Temperate grasslands include Pampas (Argentina), Prairie (North America), Veld (South Africa), Steppe (Central Asia), and Downs (Australia).
PLATE TECTONICS
- Convergent boundaries are zones where crust is destroyed as one plate subducts beneath another.
- The place where one plate sinks below another is called a subduction zone.
- Convergence occurs between an oceanic–continental plate, two oceanic plates, and two continental plates.
- Divergent boundaries are zones where new crust is created as plates move away from each other.
- Spreading sites are locations where plates move apart.
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is the best-known example of a divergent boundary separating American plates from Eurasian and African plates.
- Transform boundaries are zones where crust is neither created nor destroyed as plates slide horizontally.
EARTH MOVEMENTS
- Orogeny is the process of mountain building.
- Epeirogeny is the process of continental building. [ Trick : E-CB ]
🪨 ROCKS (GENERAL)
- Rocks do not have a definite chemical composition.
- Igneous rocks include granite, gabbro, pegmatite, basalt, volcanic breccia, and tuff.
- Sedimentary rocks include sandstone, conglomerate, limestone, shale, loess, chert, halite, and potash.
- Metamorphic rocks include gneiss, slate, schist, and marble.
- Mineral richness is greater in igneous rocks than sedimentary rocks.
CLIMATOLOGY
- Tropical cyclones mostly form on the western margins of oceans.
- Tropical cyclones do not form in eastern tropical oceans due to cold currents lowering sea surface temperature.
ATMOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE
- The troposphere is the lowest atmospheric layer and contains about 80% of atmospheric mass and 99% of water vapour and aerosols.
- Nearly 59% of water falling on land returns to the atmosphere through evaporation.
TIDES
- Spring tides occur when the sun, moon, and earth are in a straight line.
- Spring tides occur twice a month during full moon and new moon.
- Neap tides occur when the sun and moon are at right angles to each other.
- Neap tides occur about seven days after spring tides.
- The moon’s gravitational pull is stronger than the sun’s but is reduced during neap tides due to counteracting forces.
- The period when sea level falls from high tide to low tide is called ebb.
INDIAN CLIMATE
- Chillai Kalan is a 40-day period of severe winter in Kashmir.
- Chillai Kalan occurs from 21 December to 29 January.
GEOGRAPHY THOUGHT
- Geography studies the areal differentiation of the earth’s surface (Richard Hartshorne).
- Geography studies differences of phenomena related to different parts of the earth’s surface (Hettner).
🪨 STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY
- Clastic dikes are formed when sediments fill pre-existing cracks.
DESERTS
Hot Deserts
- Mojave Desert lies in California.
- Sonoran Desert lies in Mexico and the USA.
- Chihuahuan Desert lies in Mexico and the USA.
- Sechura Desert lies in Peru.
- Sahara Desert lies in Africa.
- Kalahari Desert lies in Namibia, South Africa, and Botswana. [ Trick : Kalahari : BNS ]
- Danakil Desert lies in Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Djibouti. [ Trick : D : D EE ]
- Arabian Desert lies in the Arabian Peninsula.
- Thar Desert lies in India.
- Great Victoria, Gibson, Great Sandy, Tanami, and Simpson deserts lie in Australia.
Cold Deserts
- Great Basin Desert lies in North America.
- Patagonian Desert lies in Argentina, Chile, and Falkland Islands.
- Karakum Desert lies in Turkmenistan.
- Kyzylkum Desert lies in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan.
- Taklamakan Desert lies in China.
- Gobi Desert lies in Central Asia. [ Both Mongolia and northern China ] [ Note : Very IMP Asked in UPSC ]
- Ordos Desert lies in China.
- Arctic Desert lies in polar regions.
Coastal Deserts
- Atacama Desert lies in Chile.
- Namib Desert lies in southwestern Africa.
[ Note : Namib Desert is mostly in Namibia, covering its entire coastline, but it also extends north into Angola and south into South Africa, making it a shared desert ecosystem. While the famous Namib Sand Sea is a UNESCO site located entirely within Namibia's Namib-Naukluft Park, the broader Namib Desert spans parts of three southern African countries ]
MISCELLANEOUS
- Africa has 16 landlocked countries.
- Basalt is an igneous rock.
- Slate is a metamorphic rock.
- Black soil is formed after volcanic eruptions.
- Red soil supports tobacco cultivation.
- Red soil is formed from metamorphic and igneous rocks.
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & GEOLOGY
- Clastic dikes are formed when sediments fill a pre-existing crack.
- The period between high tide and low tide when sea level is falling is called ebb.
- Mineral richness : igneous rocks > sedimentary rocks
SOILS IN INDIA
- In India, Inceptisols (39.4%) > Entisols (28%) > Alfisols > Vertisols
- Khadar region is an area where soils are naturally rejuvenated every year.
- Khadar region is low-lying, flood-prone, and affected by waterlogging.
- New alluvial soil is deposited annually in the Khadar region by floods.
SOIL CONSERVATION METHODS
- Shelterbelts are rows of trees planted in coastal and dry regions to reduce wind movement and protect soil cover.
- Terrace farming is a soil conservation method practised on hilly terrains.
SOIL CHEMISTRY
- Soil becomes acidic due to the presence of hydrogen ions (H⁺).
- Oceans become acidic due to increased carbon dioxide (CO₂). [ Highly IMP ]
- Leaching decreases soil fertility due to excessive irrigation or floods.
- Drip irrigation can reduce leaching losses.
- Fertigation involves dissolving pesticides in drip irrigation.
SOIL TYPES & CROPS
- Red soil is formed by weathering of metamorphic and igneous rocks.
- Red soil supports cotton, tobacco, wheat, potatoes, and fruits. [ Trick : Red Tobacco ]
- Yellow soil of Odisha and Chhattisgarh supports sugarcane, rice, corn, mangoes, and oranges.
- Black soil supports groundnut, cotton, wheat, jowar, and chillies.
- After volcanic eruptions, weathering and cooling of lava results in black soil formation.
- Black basalt soil of the Deccan Plateau is rich in humus, iron, magnesia, lime, and alumina.
SOIL SCIENCE & AGRICULTURE
- Pedology is the study of soils.
- Cash crops include coffee, sugarcane, peanuts, cotton, tobacco, rubber, and banana.
- In the quincunx system, trees are planted at four corners of a square with one plant in the centre.
- Papaya and pineapple are examples of crops grown using the quincunx system.
EFFECTS OF EXCESSIVE IRRIGATION
- Excessive irrigation increases soil salinity and alkalinity.
- Excessive irrigation leads to waterlogging.
- Excessive irrigation hinders air circulation in soil.
- Excessive irrigation reduces soil temperature.
- Excessive irrigation causes shallow root development.
- Excessive irrigation leads to marshy land formation.
- Excessive irrigation increases nitrate formation.
- Excessive irrigation increases soil acidity.
SOIL PARTICLE SIZE
- Soil particle size decreases in the order: rock > gravel > sand > silt > clay.
AGRICULTURE STATISTICS
- The first Agriculture Census in India was conducted in 1970–71.
- The 11th and current Agriculture Census was conducted in 2021–22.
INDIAN GEOGRAPHY
- Gulf of Mannar is known as a biological paradise.
- The Deccan Plateau slopes from west to east.
- Most rivers of the Deccan Plateau flow from west to east.
- The Deccan Plateau extends into the north-east covering Meghalaya, Karbi-Anglong Plateau, and North Cachar Hills.
- Garo, Khasi, and Jaintia hills are the prominent ranges from west to east.
DECCAN PLATEAU
- The Deccan Plateau extends over eight Indian states.
- The term “Deccan” is derived from the Sanskrit word Dakshina meaning south.
- The Deccan Plateau lies between the Western and Eastern Ghats south of the Narmada River.
- It is bounded by the Western Ghats in the west, Eastern Ghats in the east, and Satpura, Maikal, and Mahadeo hills in the north.
- The Deccan Plateau is volcanic in origin with step-like lava layers.
- It is suitable for cotton cultivation and rich in mineral resources.
- The Deccan Plateau is an important source of hydroelectric power.
ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT
- The term ecology was first used by German zoologist Ernst Haeckel in 1869 as ‘oekologie’.
EFFECTS OF EARTHQUAKES
- Earthquakes cause soil liquefaction.
- Earthquakes result in ground lurching.
- Earthquakes trigger avalanches.
- Earthquakes may cause floods due to dam and levee failures.
- Earthquakes can lead to fires.
- Earthquakes can generate tsunamis.
🪨 GEOLOGY & GEOMORPHOLOGY
- Foliated sedimentary rocks are found in Antietam National Battlefield, Maryland.
- Foliated sedimentary rocks are also found in Harpers Ferry National Historical Park, Maryland and West Virginia.
INDUSTRIAL GEOGRAPHY
- Osaka is a centre of cotton textile industry.
- Detroit is a major automobile manufacturing centre.
- Cuba is famous for cigar production.
- St. Petersburg is known for shipbuilding.
LIMNOLOGY
- The limnetic zone is the most photosynthetically active zone of a lake.
- The limnetic zone is the primary habitat of planktonic species.
- Phytoplankton are microscopic floating organisms present in the upper illuminated layer of water.
VOLCANOES
- Mount Rainier is located in the USA.
- Mount Etna is located in Italy.
- Mount Parícutin is located in Mexico.
- Mount Apo is located in the Philippines.
ISLANDS (WEST TO EAST)
- Sumatra, Java, Bali, and Lombok are arranged from west to east.
TRIBES / ETHNIC GROUPS
- Koryaks are found in Russia.
- Punan tribe is found in Borneo.
- Ruwallah tribe is found in Arabia.
- Lapps are found in Finland and Sweden.
- Jews are found in Israel.
- Teda are found in Libya.
- Beja are found in Egypt.
- Lur are found in Iran.
RIVERS
- Teesta River was earlier a tributary of the Ganga and is now a tributary of the Brahmaputra.
AGRICULTURE & HORTICULTURE
- Citrus fruits are associated with the Mediterranean region.
MOUNTAINS
- Mount Chimborazo is located in Ecuador.
- Pyrenees Mountains lie between Spain and France.
CLIMATOLOGY
- Taifu is associated with Japan.
- Baguio is associated with the Philippines.
NATURAL VEGETATION
- Epiphytes are found in equatorial regions.
- Acacia is characteristic of savanna vegetation.
- Baobab is found in the Sahara region.
- Cedars are found in the Mediterranean region.
INDIAN PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
- The Damodar River is famous for fault valley drainage.
- Savanna or tropical grassland region is known as the “big game country” or “land of safari”.
SOIL RICHNESS & CHARACTERISTICS
- Red soil is rich in iron oxide, iron, and aluminium and is acidic in nature.
- Red soil is derived from crystalline and metamorphic rocks.
- Black soil (regur) is rich in magnesium, lime, iron, and organic matter.
- Black soil is poor in nitrogen and phosphoric content.
- Black soil has the highest water-holding capacity.
- Laterite soil is rich in iron and aluminium.
- Laterite soil is deficient in nitrogen and potash.
- Laterite soil forms due to high rainfall and high temperature.
- Alluvial soil is rich in potash and poor in phosphorus.
- Arid soil has high concentration of gypsum, calcium carbonate, and sodium.
- New alluvial soil is called Khadar.
- Old alluvial soil is called Bhangar.
- Alluvial soil is the most widely available soil in India.
- Alluvial soil is found in northern plains, river valleys, deltas, and estuaries of peninsular India.
NUTRIENT DEFICIENCY IN SOILS
- Phosphorus-deficient soils include alluvial and black soils.
- Nitrogen-deficient soils include black and laterite soils.
- Potash-deficient soil is laterite soil.
MNEMONIC
GEOLOGICAL TIME SCALE
- The Mesozoic Era is known as the Age of Reptiles.
ASTRONOMY
- Proxima Centauri is the nearest star to the Earth.
- Alpha Centauri is the nearest star system to the Sun.
- Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky and is also called the Dog Star.
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
- The Congo Basin is called the Heart of Africa and is the world’s largest carbon sink.
- Laterite erosion in Jharkhand results in the deposition of bauxite.
- Kerala is the largest producer of thorium in India.
- Marmagao Port in Goa is the main iron ore exporting port of India.
RIVERS OF INDIA (ODISHA FOCUS)
- The Brahmani River is formed by the confluence of the Sankh and South Koel rivers near Rourkela.
- Rengali Dam is located at Angul on the Brahmani River.
- Samal Barrage is located at Talcher on the Brahmani River.
- The origin of the Brahmani River is mythologically associated with Sage Parashara and Satyavati, the mother of Ved Vyasa.
BAITARANI RIVER (IN NEWS)
- The Baitarani River originates from the Gonasika or Guptaganga hills in Keonjhar district.
- The river starts flowing over a stone shaped like a cow’s nostril.
- The left canal of the Baitarani River under the Anandpur Barrage was inaugurated in Keonjhar district in 2023.
- A 28 km canal connecting the Baitarani and Salandi rivers provides irrigation to 2,221 hectares in Hatadihi and Anandpur blocks.
- The Haladia Dam is part of the Subarnarekha irrigation project.
- A barrage over the Khairi Bhandan River was planned at Anlabani village in Mayurbhanj district.
INDIAN PHYSIOGRAPHY
- Karbi Anglong Plateau is an extension of the Peninsular Plateau.
LADAKH GEOGRAPHY
- Ladakh is known for its ancient monasteries called gompas.
- Hemis, Thiksey, and Diskit are famous monasteries of Ladakh.
- Nubra Valley, Pangong Tso, and Tso Moriri are famous meadows and landscapes of Ladakh.
ISLAND GEOGRAPHY
- Lakshadweep is a uni-district Union Territory.
- Lakshadweep consists of 36 islands, 12 atolls, 3 reefs, 5 submerged banks, and 10 inhabited islands.
VEGETATION & ENVIRONMENT
- Eucalyptus grows in high rainfall areas and on steep slopes prone to landslides.
🪨 GEOLOGY (BASIC NOTES)
- Igneous plus metamorphic rocks are more resistant than sedimentary rocks.
- Rock types include igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
- Diastrophism refers to large-scale deformation of the Earth’s crust.
SOIL & IRRIGATION
- Excessive irrigation increases nitrate formation in soil.
- Excessive irrigation increases soil acidity.
PLATEAUS & HILLS (RAJASTHAN)
- Oriya Plateau is located in Sirohi, Rajasthan.
- Plateau of Mesa or Hill of Bika is located in Chittorgarh.
- Plateau of Kraska is located in Alwar.
- Tirkut Hill is located in Jaisalmer.
SEDIMENTARY ROCK DISTRIBUTION
| Type of Sedimentary Rock | Location | Region / Country |
|---|
| Non-foliated sedimentary rocks | Rock Creek Park | District of Columbia, USA |
| Non-foliated sedimentary rocks | City of Rocks National Reserve | Idaho, USA |
| Foliated sedimentary rocks | Antietam National Battlefield | Maryland, USA |
| Foliated sedimentary rocks | Harpers Ferry National Historical Park | Maryland & West Virginia, USA |
INTERNATIONAL BOUNDARIES & LINES
| Boundary / Line | Countries Separated |
|---|
| Oder–Neisse Line | Germany – Poland |
| 38th Parallel | North Korea – South Korea |
| Maginot Line | France – Germany |
| Durand Line | Pakistan – Afghanistan |
| Blue Line | Lebanon – Israel |
| 49th Parallel | United States – Canada |
| 31st Parallel | Iran – Iraq |
| 25th Parallel | Mali – Mauritania |
| 22nd Parallel | Sudan – Egypt |
| 17th Parallel | North Vietnam – South Vietnam |
| Hindenburg Line | Germany – Poland |
| Mannerheim Line | Finland – Russia |
| Attila Line / Green Line | Turkish Cyprus – Republic of Cyprus |
| Siegfried Line | Germany – France |
MINERAL PRODUCTION (MAJOR REGIONS)
| Region / Town | Mineral Produced | Country |
|---|
| Postmasburg (Northern Cape) | Manganese | South Africa |
| Kinta Valley | Tin | Malaysia |
IRON ORE PRODUCING AREAS
| Region | Country |
|---|
| Karaganda | Kazakhstan |
| Krivoy Rog | Ukraine |
| Normandy | France |
| Pyrenees | France |
ECONOMIC GEOLOGY
| Region | Resource Significance |
|---|
| Pegu Yoma | Oil-rich region |
WORLD IRON MINES (Country-wise Grouping)
| Country | Iron Mines |
|---|
| Australia | Hamersley Mines, Channar, Newman, Jimblebar |
| Canada | Mount Wright, Carol Lake |
| Russia | Lebedinsky |
| Brazil | Minas Centrais |
RIVERS & WETLANDS
- Bhagirathi–Bhilangna is a major tributary of the Ganga.
- Ningnag Wetland (Kashmir) is a tectonic wetland.
- Rudrasagar Lake (Tripura) is a sedimentation reservoir.
- Loktak Lake (Manipur) is an oxbow-type wetland.
- Renuka Lake (Himachal Pradesh) is the smallest Ramsar wetland in India.
SOILS IN INDIA
- Soil distribution in India: Inceptisols (39.4%) > Entisols (28%) > Alfisols > Vertisols.
FOREST LEGISLATION (INDIA)
- 1855: Forest conservation rules introduced by Lord Dalhousie.
- 1894: First National Forest Policy under Lord Elgin.
- 1952: National Forest Policy after independence (amended in 1988).
- Target: 33% forest cover of total geographical area.
PASSES & LATITUDES
- Khardung La Pass is among the highest motorable passes in the world.
- Tropic of Cancer is shortest in Gujarat and longest in Madhya Pradesh.
- Tropic of Cancer passes through 8 Indian states.
- Globally, it passes through 17 countries, 3 continents, and 6 major water bodies.
COUNTRIES & AGRICULTURE
- Chile is the world’s longest north–south country.
- Iran is the largest producer of saffron, followed by India.
WINDS & ATMOSPHERIC TERMS
- Doldrums are the belt of calm near the equator.
- Coriolis force causes deflection of winds.
- Roaring Forties are strong westerlies in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Harmattan is a dry, dust-laden wind of West Africa known as the “Doctor Wind”.
FOLD MOUNTAINS (EXAMPLES)
- Major fold mountains include Himalayas, Andes, Alps, Urals, Appalachians, Atlas, Hindukush.
IMPORTANT PEAKS
- Rocky Mountains: Mount Elbert
- Appalachians: Mount Mitchell
- Alps: Mont Blanc (source region of Rhine & Danube)
- Scandinavian Range: Galdhøpiggen
- Carpathians: Gerlachovský Štít
- Ural Mountains: Mount Narodnaya
- Sierra Nevada: Mount Whitney
- Alaska Range: Mount McKinley (Denali)
- Andes: Mount Aconcagua (longest mountain chain)
- Atlas Mountains: Mount Toubkal
- Altai Mountains: Mount Belukha
- Drakensberg: Highest peak in Lesotho
- Hindukush: Tirich Mir
- Arakan Yoma: Mount Kennedy
- Kunlun Range: Mount Muztagh Ata
- Dhaulagiri means “White Mountain” (Nepal).
TRIBES & ETHNIC GROUPS
- Bushmen: Namibia
- Pygmies: Congo Basin (Zaire)
- Eskimos (Inuit): Alaska
OCEANOGRAPHY
- Ocean salinity is highest near the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn.
TIME ZONES
- France has the maximum number of time zones (13), including overseas territories.
GEOLOGY & CLIMATOLOGY
- Foliation is the alignment of minerals into layers during metamorphism.
- Dendroclimatology studies past climate using tree rings.
INDIAN HILLS & RANGES
- Mizo (Lushai) Hills: Mizoram
- Patkai Hills: Part of Purvanchal Range
- Mishmi Hills: Arunachal Pradesh
- Abor Hills: Arunachal Pradesh
- Mikir Hills: Assam
- Mount Tiyi: Nagaland