A Decade of Growth with PM Mudra Yojana

IN NEWS: A Decade of Growth with PM Mudra Yojana
ANALYSIS
1. Context
- India completes 10 years of the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) on 8 April 2025.
- The scheme was launched in April 2015 to “Fund the Unfunded” by providing collateral-free loans to micro and small enterprises.
- It has emerged as a key driver of grassroots entrepreneurship, financial inclusion, and women-led development.
2. Key Achievements
A. Credit Outreach and Expansion
- 52 crore loans sanctioned since 2015 worth ₹32.61 lakh crore.
- Loans enable micro entrepreneurs across sectors such as tailoring, trading, services, repair shops, manufacturing and more.
- PMMY supports non-corporate, non-farm small units that form the base of India’s economic pyramid.
B. Impact on MSME Credit Ecosystem
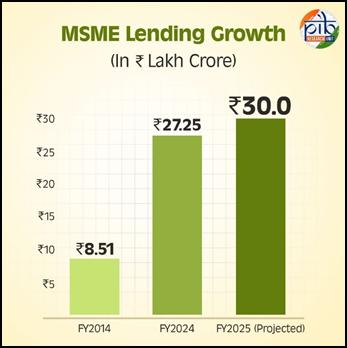
- MSME lending rose from ₹8.51 lakh crore (FY14) to ₹27.25 lakh crore (FY24); projected to cross ₹30 lakh crore (FY25).
- MSME share of total bank credit rose to ~20% in FY24.
- Growth driven significantly by greater formalisation, accessibility and confidence created by Mudra loans.
C. Women Empowerment
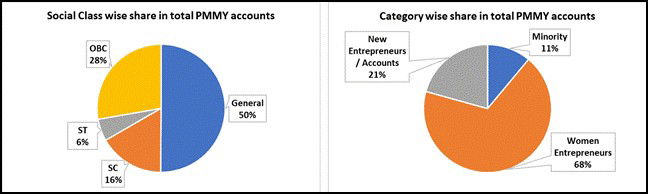
- Women constitute 68% of total Mudra beneficiaries.
- Per woman disbursement rose at a CAGR of 13% (FY16–FY25).
- States with high female disbursement recorded higher employment generation via women-led MSMEs.
- Greater participation supports labour force inclusion and household financial security.
D. Financial Inclusion for Marginalised Communities
- 50% of Mudra accounts belong to SC/ST/OBC entrepreneurs.
- 11% of loan accounts belong to minority communities.
- This indicates strong social inclusion by enabling first-time formal borrowers.
E. Shift from Micro to Small Enterprises
- Kishor loans (₹50,000–₹5 lakh) increased from 5.9% in FY16 to 44.7% in FY25.
- Tarun loans (₹5–10 lakh) also increasing, indicating business scaling.
- Average loan size tripled from ₹38,000 (FY16) → ₹72,000 (FY23) → ₹1.02 lakh (FY25).
F. State/UT-Level Performance
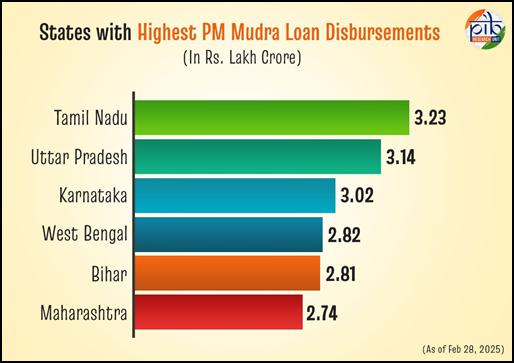
Top Disbursing States (as of 28 Feb 2025)
- Tamil Nadu – ₹3,23,647.76 crore
- Uttar Pradesh – ₹3,14,360.86 crore
- Karnataka – ₹3,02,146.41 crore
- West Bengal – ₹2,82,322.94 crore
- Bihar – ₹2,81,943.31 crore
- Maharashtra – ₹2,74,402.02 crore
Top UT:
- Jammu & Kashmir – ₹45,815.92 crore across 21,33,342 loan accounts.
G. International Recognition
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) acknowledged PMMY in:
- 2017 – Noted strong role in enabling women-led businesses.
- 2019 – Recognised its role in developing and refinancing micro enterprises.
- 2023 – Highlighted growth in women-owned MSMEs (over 2.8 million).
- 2024 – Praised India’s enabling entrepreneurship ecosystem supported by PMMY.
3. Mission and Scheme Design
A. Purpose
- Provide collateral-free institutional credit to micro units.
- Strengthen self-employment and grassroots livelihoods.
B. Implementing Agency
- Micro Units Development and Refinancing Agency (MUDRA) — created by Government of India.
C. Eligible Lending Institutions
- Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs)
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- NBFCs
- MFIs
D. Loan Categories (Interventions)
- Shishu – Up to ₹50,000
- Kishor – ₹50,000 to ₹5 lakh
- Tarun – ₹5 lakh to ₹10 lakh
- Tarun Plus – Above ₹10 lakh to ₹20 lakh (for Tarun beneficiaries with successful repayment)
4. Broader Significance
- PMMY has formalised informal credit for millions.
- Enhanced self-employment, local job creation, and economic decentralisation.
- Created confidence among first-time borrowers, women entrepreneurs, rural youth and socially marginalised groups.
- Strengthened India’s shift from job-seeking to job-creating economy.
STATIC PART (Relevant Concepts)
- MUDRA (Micro Units Development and Refinance Agency) – A government agency that refinances microfinance institutions and banks for lending to micro businesses.
- Collateral-free loans – Loans without security; guaranteed under programmes like Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro Units (CGFMU).
- MSMEs – Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises; major sources of employment and economic output.
- Financial Inclusion – Ensuring access to financial services at affordable cost for all sections of society.
- IMF – International Monetary Fund; global institution monitoring financial stability, growth and economic policy.