A Holistic Approach for Cleanliness of River Ganga
IN NEWS
A Holistic Approach for Cleanliness of River Ganga
ANALYSIS
1. Context
- The Namami Gange Programme (NGP), launched in 2014–15, is India’s flagship river rejuvenation mission.
- Initially approved in June 2014 with a ₹20,000 crore outlay, later extended to March 2026 with ₹22,500 crore.
- Focus: Pollution abatement, conservation, and rejuvenation of the Ganga and its tributaries.
2. National Ganga Plan – Budget 2025–26
- ₹3,400 crore allocated for FY 2025–26.
- Target areas:
- Improve sewage treatment capacity
- Enhance water quality
- Regulate industrial waste
- Achieve prescribed bathing standards by 2025
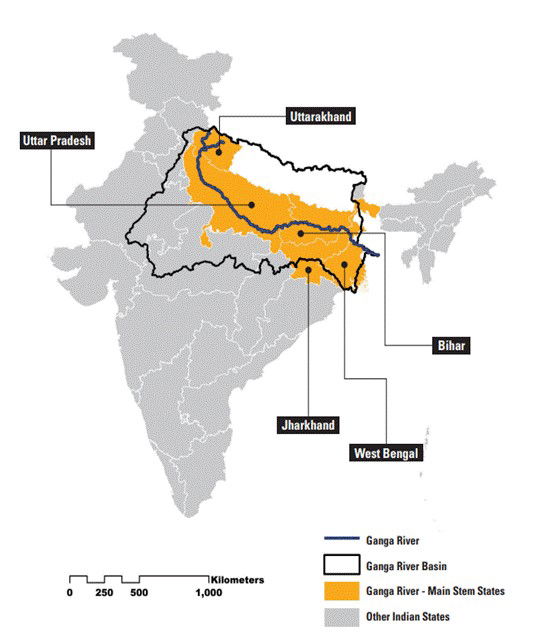
3. Ganga River Basin – Key Facts
- Basin covers 27% of India’s landmass; spans 11 states.
- Supports 47% of India’s population.
- Land use:
- 65.57% agriculture
- 3.47% water bodies
- Despite receiving 35.5% of total precipitation, it is the second most water-stressed basin after Sabarmati.
- Receives only 39% of average per capita annual rainwater input among major Indian basins.
4. Vision for Ganga Rejuvenation
Based on the Ganga River Basin Management Plan (GRBMP) prepared by seven IITs, focusing on:
- Aviral Dhara – Continuous flow
- Nirmal Dhara – Unpolluted flow
- Preservation of geological and ecological integrity
- Emphasis on Integrated River Basin Management (IRBM) – multi-agency & multi-sectoral coordination
5. Key Interventions
A. Pollution Abatement (Nirmal Ganga)
- Reduction of point & non-point pollution sources
- Sewage treatment expansion
- Industrial effluent regulation
B. Improving Ecology and Flow (Aviral Ganga)
- River flow management
- Ecological restoration
C. Strengthening People–River Connect (Jan Ganga)
- Community participation
- Awareness activities
D. Research & Policy Support (Gyan Ganga)
- Evidence-based policymaking
- Scientific studies & mapping
- Institutional strengthening
6. Project Progress (As of 31 January 2025)
Overall
- 492 projects worth ₹40,121.48 crore sanctioned
- 307 projects completed
Sewage Infrastructure
- 206 projects undertaken
- Sanctioned amount: ₹33,003.63 crore
- 127 STPs completed → major impact on pollution load
Biodiversity & Afforestation
- 56 projects taken up
- Funding: ₹905.62 crore
- 39 projects completed
- Focus on ecological recovery of the basin
7. Recent Government Approvals
A. Varanasi Project
- ₹274.31 crore sanctioned
- Interception & diversion of Durga Drain
- Construction of 60 MLD STP (Hybrid Annuity Model)
- Includes a 75 MLD main pumping station
B. Bhadohi Initiative
- ₹127.26 crore investment
- Prevention of untreated sewage into Varuna River
- Three STPs: 17 MLD, 5 MLD, 3 MLD
- DBOT model with 15 years O&M
- Sewer networks to capture four major drains
C. Reuse of Treated Wastewater
- National Framework developed for States
- Guidance handbook to promote safe reuse
- Supports freshwater conservation & sustainable water management
D. Biodiversity Initiatives
- 7 Biodiversity Parks approved in UP
- 5 priority wetlands sanctioned (UP – 3, Bihar – 1, Jharkhand – 1)
- Forestry intervention:
- 33,024 ha afforested
- ₹398 crore expenditure
E. Fish Biodiversity Conservation
- 143.8 lakh Indian Major Carp fingerlings released since 2017
- Supports:
- Fish biodiversity
- River dolphin prey base
- Livelihoods of basin fishers
F. Industrial Pollution Abatement
- 3 CETPssanctioned:
- Jajmau CETP (20 MLD)
- Banther CETP (4.5 MLD)
- Mathura CETP (6.25 MLD)
- Completed:
- Mathura CETP (6.25 MLD)
- Jajmau CETP (20 MLD)
8. Sewage Infrastructure – Key Numbers
- 203 sewage infrastructure projects (₹32,613 crore)
- 6255 MLD total treatment capacity
- 127 STPs operational with 3446 MLD capacity
9. Overall Significance
- Reduction in sewage flow & industrial discharge
- Improved river health parameters
- Strengthening ecosystem & biodiversity
- Community involvement in river conservation
- Major step towards achieving bathing-quality standards
- Long-term river basin sustainability through IRBM
STATIC PORTION
- Namami Gange launch: 2014–15
- Implementing Agency: National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG)
- Parent Ministry: Ministry of Jal Shakti
- Key Components: Aviral, Nirmal, Jan Ganga, Gyan Ganga
- Funding Models: Hybrid Annuity Model (HAM), DBOT
- Basin Coverage: 27% landmass, 47% population
- Major Tributary Mentioned: Varuna
- Ganga Basin Stress: Second most water-stressed after Sabarmati


Updated – 07 Mar 2025 ; 3:42 PM | PIB
News Source: PIB (https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2109078)