Budget 2025-26: Fuelling MSME Expansion
In News
The Union Budget 2025–26 has placed strong emphasis on strengthening the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector—acknowledging it as a pillar of inclusive economic growth, employment generation, and exports.The Budget introduces major policy measures to expand access to credit, raise classification limits, boost labour-intensive sectors, and support first-time entrepreneurs, particularly from disadvantaged communities.
Background: MSME Landscape in India
| Parameter | Data |
|---|---|
| Registered MSMEs (Udyam Portal) | 5.93 crore |
| Employment generated | 25+ crore individuals |
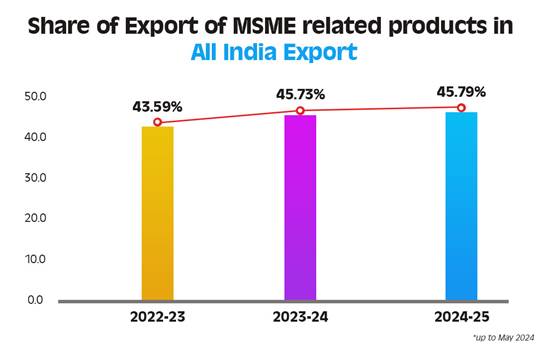
| Share in India’s exports (2023–24) | 45.73% |
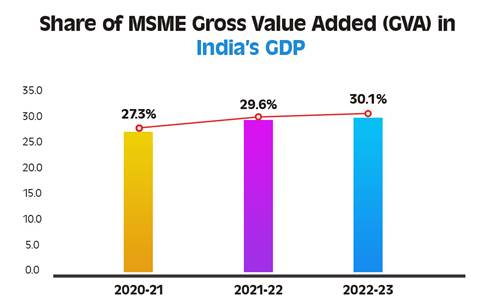
| Share in GVA (2022–23) | 30.1% |
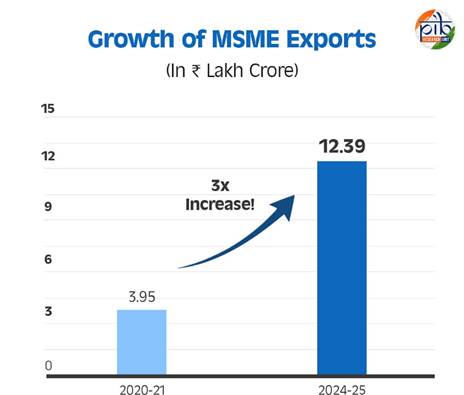
| MSME exports | ₹12.39 lakh crore (2024–25) |
Significance:
MSMEs are vital to India's manufacturing base, self-employment generation, rural industrialization, and Atmanirbhar Bharat vision.
Key Budgetary Announcements for MSMEs (2025–26)
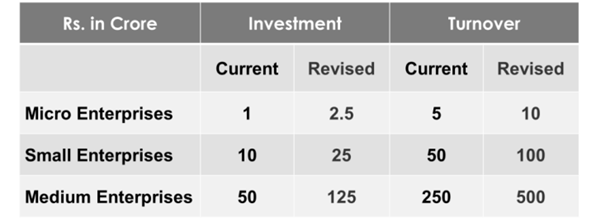
1. Revised Classification Criteria
- Investment limit increased by 2.5 times and turnover limit by 2 times.
- Objective: enable MSMEs to scale operations, adopt advanced technologies, and create more jobs.
→ Significance: Prevents premature graduation from MSME category and encourages sustained expansion.
2. Enhanced Credit Availability
- Credit Guarantee cover for Micro & Small Enterprises: ₹5 crore → ₹10 crore (additional ₹1.5 lakh crore credit over 5 years).
- Startups: Guarantee cover doubled to ₹20 crore, with reduced fees.
- Exporter MSMEs: Access to term loans up to ₹20 crore with enhanced guarantee.
- Credit Cards for Micro Enterprises: ₹5 lakh credit limit for 10 lakh micro units via Udyam portal.
→ Impact: Expands access to formal credit and reduces dependency on informal lending—especially for rural & micro enterprises.
3. Focus on Inclusive Entrepreneurship
- Fund of Funds (₹10,000 crore) to promote startups and innovation.
- Scheme for first-time entrepreneurs (Women, SC/ST): Term loans up to ₹2 crore for 5 years, inspired by Stand-Up India.
→ Impact: Encourages social inclusion, first-generation entrepreneurship, and women-led growth.
4. Support to Labour-Intensive Sectors
- Footwear & Leather Sector:Focus Product Scheme to support design, non-leather production & component manufacturing.
- Expected: 22 lakh jobs, ₹4 lakh crore turnover.
- Toy Sector: Cluster development & skilling for global market competitiveness.
- Food Processing: New National Institute of Food Technology, Entrepreneurship & Management in Bihar.
→ Impact: Employment generation, regional development, and diversification of exports.
5. Manufacturing & Clean-Tech Mission
- National Manufacturing Mission: Policy roadmap for small, medium & large industries.
- Clean-Tech Focus:Incentives for domestic manufacturing of
- Solar PV cells
- EV batteries
- Wind turbines
- High-voltage transmission equipment
→ Impact: Strengthens India’s push for green industrialisation, energy security, and global competitiveness.
6. Budgetary Allocation Trend (₹ Crore)
| Year | Budget Estimates | Revised Estimates |
|---|---|---|
| 2022–23 | 21,422 | 23,628 |
| 2023–24 | 22,137 | 22,138 |
| 2024–25 | 22,137 | 17,307 |
| 2025–26 | 23,168 | — |
📊 Sustained allocation growth reflects renewed fiscal commitment to MSME revival post-COVID.
Supporting Flagship Schemes
| Scheme | Objective | Key Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| PM Vishwakarma | Support artisans & traditional craftspeople | ₹13,000 crore outlay (2023–28), 2.65 crore applications |
| Udyam Portal | Simplified registration for enterprises | 5.93 crore MSMEs registered |
| PMEGP | Credit-linked subsidy for micro-enterprises | 89,118 enterprises supported in 2023–24; 7.1 lakh jobs |
| SFURTI | Cluster development for traditional industries | 376 functional clusters; 2.2 lakh artisans |
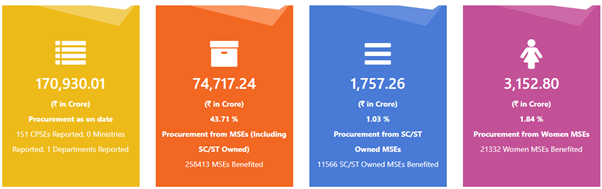
| Public Procurement Policy (2012) | 25% of CPSE purchases reserved for MSEs | ₹74,717 crore procurement (2023–24); 43.71% share |
Analytical Insights
1. Economic Implications
- Boosts credit penetration and formalisation in the MSME sector.
- Enhances export competitiveness and manufacturing base under Make in India.
- Strengthens regional industrial clusters, especially in Tier-II & Tier-III cities.
2. Social & Inclusive Growth
- Promotes women-led and SC/ST entrepreneurship, aligning with Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas.
- Encourages first-generation entrepreneurs through easier credit and training.
3. Governance & Policy Reform
- Integration of schemes like Udyam Assist, Vishwakarma, and PMEGP marks a whole-of-government approach.
- The credit card initiative for micro enterprises mirrors global best practices in SME financing.
Challenges Ahead
- Credit Absorption Gap: Despite reforms, many MSMEs lack collateral or credit history.
- Delayed Payments: Cash flow disruptions due to pending dues from PSUs and corporates.
- Technology Upgradation: Need for digital adoption and R&D incentives.
- Informal Sector Integration: Over 80% of micro enterprises remain unregistered.
- Market Access: Export compliance and logistics bottlenecks still hinder scale.
Way Forward
- 📌 Strengthen digital credit ecosystems via Udyam + Account Aggregator framework.
- 📌 Ensure timely payments under MSME Samadhan and TReDS platforms.
- 📌 Promote cluster-based skilling and local value addition.
- 📌 Expand green finance and sustainability-linked loans for MSMEs.
- 📌 Institutionalise data-driven monitoring for scheme evaluation.
🪶 Conclusion
The Union Budget 2025–26 marks a decisive shift from recovery to resilience for India’s MSME sector.
By enhancing access to credit, supporting first-time entrepreneurs, and focusing on manufacturing and clean-tech, the Budget aims to empower local enterprises to compete globally.If effectively implemented, these measures could turn MSMEs into the engine of India’s $10-trillion economy vision — driving innovation, employment, and inclusive growth.
Updated - 04 FEB 2025 5:27 PM | PIB