Chandrayaan-2 Makes First-Ever Observation of Sun’s Impact on the Moon
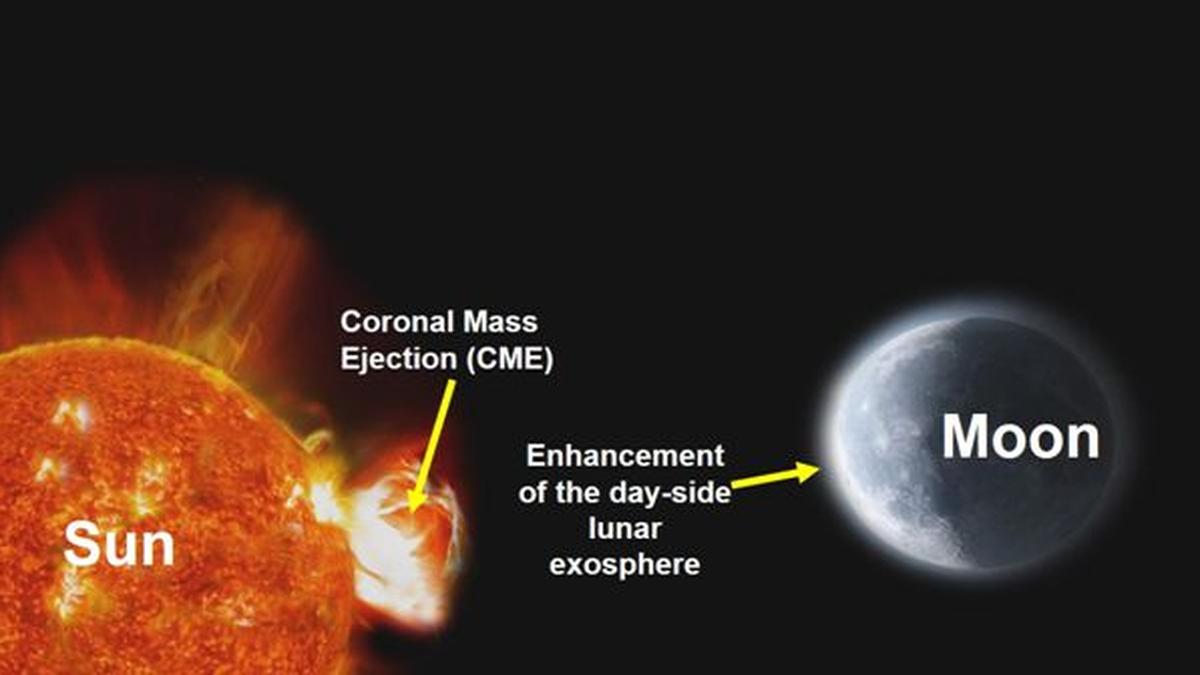
In News: Chandrayaan-2 Detects Effects of Solar Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) on Lunar Exosphere
Key Highlights:
- Observation:
- Chandrayaan-2’s CHACE-2 payload has for the first time observed the impact of a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) from the Sun on the Moon.
- The event occurred on May 10, 2024, when multiple CMEs were hurled towards the Moon.
- Findings:
- Dayside lunar exosphere pressure increased by over an order of magnitude.
- Solar CME caused atoms to be knocked off the lunar surface, temporarily increasing the density of the lunar exosphere.
- Observations match theoretical predictions but are first-time direct measurements.
- Scientific Significance:
- Provides new insights into lunar exosphere dynamics and space weather effects on the Moon.
- Highlights challenges for future lunar bases, as CMEs can temporarily alter surface conditions.
- Chandrayaan-2 Mission Overview:
- Launched on July 22, 2019 from Sriharikota using GSLV-MkIII-M1.
- Carried eight experiment payloads, including CHACE-2.
- Orbiter successfully inserted into elliptical lunar orbit; Vikram lander lost communication during soft-landing attempt.
- Implications for Lunar Science:
- Helps understand interaction between solar activity and the Moon’s surface/exosphere.
- Useful for planning human and robotic missions, ensuring safety from extreme space weather events.
Static Information:
- Payload: CHACE-2 (Chandra’s Atmospheric Composition Explorer-2)
- Observation Date: May 10, 2024
- Effect Observed: Increase in lunar exosphere pressure due to CME
- Significance: First direct observation of CME’s effect on the Moon
Updated - October 19, 2025 07:44 pm | The Hindu