Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana- National Rural Livelihoods Mission
In News
The Ministry of Rural Development released an update (PIB, 23 October 2025) highlighting the achievements and ongoing initiatives under Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM), the flagship poverty alleviation programme aimed at empowering rural communities, particularly women, through self-employment, skill development, and financial inclusion.
Analysis
- Background and Evolution
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM) was launched in 2010 by restructuring the Swarnajayanti Grameen Swarojgar Yojana (SGSY).
- In 2016, it was renamed Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM).
- Implemented by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) as a centrally sponsored scheme jointly funded by the Centre and States.
- It is one of the world’s largest livelihood programmes aimed at reducing poverty by promoting gainful self- and wage-employment.
- Mission Objective
- Mobilize rural poor households into Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- Promote financial inclusion, sustainable livelihoods, and access to social entitlements.
- Facilitate access to credit and diversification of income sources to ensure a sustainable rise in living standards.
- Major Achievements (As of 2025)
- 10.05 crore rural households mobilized into 90.9 lakh SHGs across 28 States and 6 UTs.
- ₹11 lakh crore credit disbursed to SHGs with a 98% repayment rate, facilitated by Bank Sakhis.
- 4.62 crore Mahila Kisans supported through farm-based livelihood initiatives.
- 47,952 Bank Sakhis deployed to improve credit linkage and financial literacy.
- 3.74 lakh enterprises promoted through the Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP).
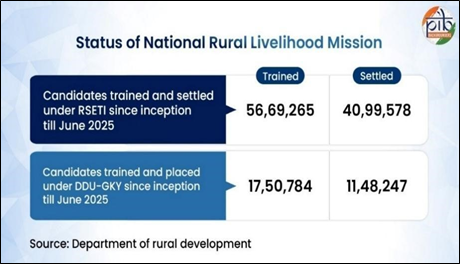
- 17.5 lakh youth trained under DDU-GKY; 11.48 lakh placed in jobs.
- 56.69 lakh trained and 40.99 lakh settled under Rural Self Employment Training Institutes (RSETI).
- 3.5 lakh Krishi Sakhis and Pashu Sakhis deployed; 6,000 Integrated Farming Clusters formed.
- Women Empowerment Focus
- Central to the mission’s strategy is organizing women into SHGs and federations for social and economic empowerment.
- Trained community resource persons such as Krishi Sakhi, Pashu Sakhi, Bank Sakhi, Bima Sakhi facilitate last-mile service delivery in agriculture, livestock, and financial inclusion.
- Women-led SHGs have become key drivers of entrepreneurship and social transformation at the grassroots.
- State-Wise Performance Highlights
- Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh — top states in SHG mobilization.
- Andhra Pradesh — leads in bank loan disbursement to SHGs (₹34,83,725 lakh).
- Uttar Pradesh and Bihar — highest capitalization support to SHGs.
- Maharashtra — top performer in agro-ecological initiatives for Mahila Kisans.
- Assam — leads in micro-enterprises under SVEP; followed by Kerala and West Bengal.
- Skill Development and Employment Components
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY):
Provides placement-linked skill training to youth aged 15–35 years.- Uttar Pradesh (2.44 lakh), Odisha (2.15 lakh), and Andhra Pradesh (1.33 lakh) lead in training numbers.
- Odisha achieved the highest placements (1.77 lakh).
- Rural Self Employment Training Institutes (RSETI):
Provides entrepreneurship and self-employment training to youth aged 18–50 years.- Uttar Pradesh leads with 7.55 lakh trained and 5.54 lakh settled entrepreneurs, followed by Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY):
- Marketing and Advanced Training Initiatives
- SARAS Aajeevika Mela 2025 held in New Delhi (5–22 September 2025) for marketing, training, and product promotion.
- NIRD&PR conducted 44 capacity-building programs in the past three years to strengthen SHG marketing capabilities.
- Impact and Significance
- DAY-NRLM has become a cornerstone of rural transformation through inclusion, capacity-building, and sustainable livelihoods.
- It has strengthened the SHG–bank ecosystem and promoted women’s financial autonomy.
- The model showcases community-led development through financial discipline, local enterprise, and participatory governance.
Static / Background Information
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Launched | 2010 (as NRLM), renamed in 2016 |
| Nodal Ministry | Ministry of Rural Development |
| Type | Centrally Sponsored Scheme |
| Funding Pattern | Jointly by Centre and States |
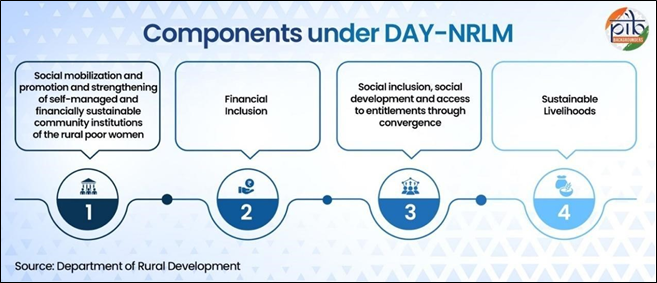
| Core Components | Social mobilization, Financial inclusion, Sustainable livelihoods, Social development and access to entitlements |
| Key Sub-Schemes | DDU-GKY, RSETI, Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP) |
| Target Group | Rural poor, especially women |
| Institutional Mechanism | SHGs, Village Organizations, Cluster Level Federations |
| Associated Programs | SARAS Aajeevika Mela, Aajeevika Grameen Express Yojana (AGEY) |


Updated - 23 OCT 2025 11:24 AM | PIB
Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana National Rural Livelihoods Mission Ministry of Rural Development Women Empowerment Self Help Groups Financial Inclusion DDU-GKY RSETI Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme SARAS Aajeevika Mela Rural Development Poverty Alleviation Community Resource Persons Mahila Kisan Krishi Sakhi Pashu Sakhi Bank Sakhi