India’s Success in Reducing Maternal Mortality
“Saving Mothers, Strengthening Futures” – India’s Success in Reducing Maternal Mortality
Source: PIB | Published on: 21 March 2025
Topic: Health – Maternal Mortality & Public Health Systems
Context
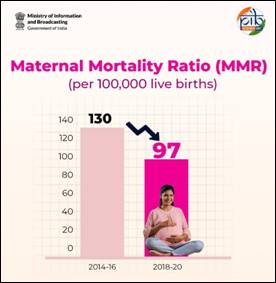
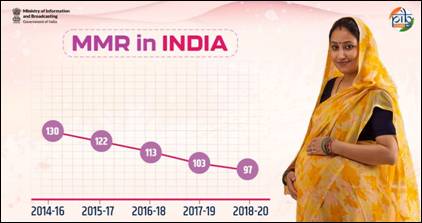
India has recorded a historic reduction in Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR), achieving the National Health Policy (NHP) 2017 target of MMR < 100 (97 per 1,00,000 live births during 2018–20) and progressing steadily towards the SDG 3.1 target of MMR < 70 by 2030.
This achievement reflects sustained government efforts under the National Health Mission (NHM) and allied maternal health schemes.
Key Data
| Indicator | NFHS-4 (2015–16) | NFHS-5 (2019–21) |
|---|---|---|
| ANC visit in 1st trimester | 59% | 70% |
| ≥4 ANC visits | 51% | 59% |
| Institutional deliveries | 79% | 89% |
| Rural institutional births | — | 87% |
| Urban institutional births | — | 94% |
- India’s MMR: 130 → 97 per 1,00,000 live births (2014–16 → 2018–20)
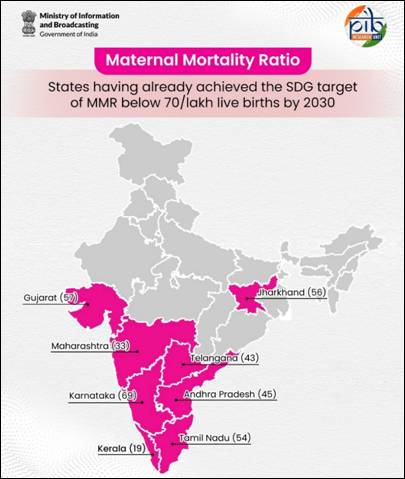
- States achieving SDG target (<70): Kerala, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Jharkhand, Gujarat, Karnataka
- 100% institutional births: Kerala, Goa, Lakshadweep, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu
Trend
- WHO certified elimination of maternal and neonatal tetanus (2015).
- Continuous decline in MMR shows improved maternal health infrastructure, awareness, and institutional care coverage.
Age-Wise Maternal Death Distribution (2018–20)
| Age Group | Maternal Deaths | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| 20–24 yrs | 32% | Highest vulnerability |
| 25–29 yrs | 30% | Significant risk period |
| 30–34 yrs | 20% | Moderate decline |
| <20 or >35 yrs | 19% | Associated with high-risk pregnancies |
Government Interventions & Schemes
1. National Health Mission (NHM) – RMNCAH+N Strategy
A holistic framework covering Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, Child, Adolescent Health & Nutrition.
2. Flagship Schemes
| Scheme | Objective / Benefit |
|---|---|
| Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) | Promotes institutional delivery among poor, SC/ST women. |
| Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY 2.0) | ₹5000 for first child; additional incentive for 2nd child if a girl (under Mission Shakti). |
| Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram (JSSK) | Free delivery (including C-section), medicines, transport, and diet. |
| Surakshit Matritva Aashwasan (SUMAN) | Dignified, assured, free maternal & newborn care; zero denial policy. |
| Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA) | Fixed-day ANC on 9th of every month; 5.9 crore+ women examined. |
| LaQshya Initiative (2017) | Improves quality of care in labour rooms and maternity OTs. |
| Anaemia Mukt Bharat (AMB) | Tackles anaemia in adolescents and pregnant women as part of POSHAN Abhiyan. |
Infrastructure & Capacity Measures
- Establishment of Maternal and Child Health (MCH) Wings, Obstetric ICUs, and First Referral Units (FRUs).
- Training of MBBS doctors in EmOC (C-section) & LSAS (Anesthesia).
- Maternal Death Surveillance Review (MDSR) at facility & community levels.
- Strengthened Comprehensive Abortion Care (CAC) services.
- Village Health, Sanitation and Nutrition Days (VHSND) for outreach maternal care.
- Use of Reproductive & Child Health (RCH) portal for name-based tracking of pregnancies and post-natal services.
Success Stories & State Innovations
| State | Initiative | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Madhya Pradesh | Dastak Abhiyan | Community-based maternal health risk detection. |
| Tamil Nadu | Emergency Obstetric Care Model | Ensures timely emergency care via robust referral systems. |
Analysis
- Determinants of progress: improved ANC coverage, institutional delivery, skilled birth attendance, and nutrition.
- Challenges remain: regional disparities (e.g., UP, Bihar, Assam), anaemia prevalence, and rural health infrastructure gaps.
- Way Forward: Focused interventions for high-burden districts, digital monitoring, adolescent health integration, and gender-sensitive community participation.
Conclusion
India has achieved the National Health Policy 2017 target (MMR < 100) and is on track to achieve the SDG 3.1 target (MMR < 70) by 2030. Sustained investment in maternal healthcare infrastructure, capacity building, and social behaviour change communication (SBCC) will be essential to ensure “No mother dies giving life.”
Updated - 21 MAR 2025 6:41 PM | PIB