PM-ABHIM : Building Pandemic-Ready Healthcare Infrastructure
IN NEWS: PM–Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM)
(PIB, 24 October 2025)
Analysis
- About the Mission
- The Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) was launched on 25 October 2021 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It is one of India’s largest pan-national health programmes with a total investment of ₹64,180 crore (2021–26).
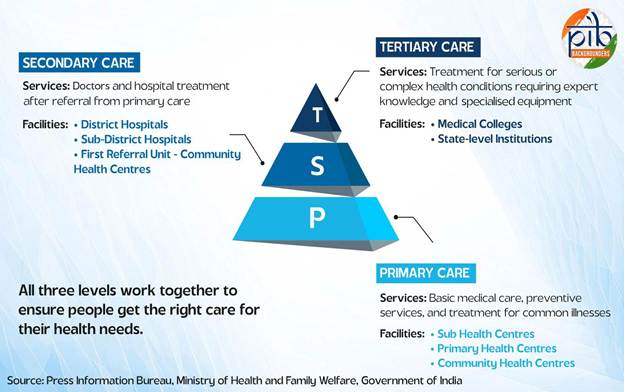
- The Mission aims to strengthen the healthcare infrastructure from the primary to tertiary levels and prepare India for future pandemics and emergencies.
- Objectives
- To create a resilient, accessible, and self-reliant public health system.
- To strengthen health facilities including Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs), Block Public Health Units (BPHUs), Integrated Public Health Labs (IPHLs), and Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- To establish a real-time, IT-enabled disease surveillance network integrated across all levels of governance.
- To promote health research and innovation based on the One Health approach, connecting human, animal, and environmental health.
- Progress and Implementation (as of 2025)
- 17,788 Sub-Health Centres approved for upgradation to AAMs.
- 11,024 Urban AAMs (U-AAMs) being set up in urban and slum areas.
- 3,382 BPHUs and 730 IPHLs (one per district) approved.
- 602 CCBs sanctioned in districts with populations over five lakh.
- Total administrative approvals worth ₹32,928.82 crore granted to States and UTs.
- Financial Allocation (₹ crore)
- Total fund allocation (2021–26): ₹64,180 crore.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS): ₹54,204.78 crore.
- Central Sector Components (CS): ₹9,339.78 crore.
- 15th Finance Commission share: ₹19,272.43 crore.
- Policy Framework and Linkages
- Builds on National Health Policy 2017 – focus on community-based health systems and local disaster preparedness.
- Strengthens foundations of National Health Mission (2005) – decentralised, community-owned health systems.
- Complements the Ayushman Bharat (2018)framework through four pillars:
- AB–PMJAY (Insurance-based secondary & tertiary care).
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs) (Primary care).
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) (Digital health records).
- PM–ABHIM (Infrastructure & pandemic preparedness).
- Global Context – WHO Pandemic Agreement (May 2025)
- WHO member states adopted the Pandemic Agreement to ensure equitable pandemic response.
- Introduced the Pathogen Access and Benefit-Sharing (PABS) system, Coordinating Financial Mechanism, and Global Supply Chain and Logistics Network (GSCL).
- Complements International Health Regulations (IHR, 2024) to improve global outbreak coordination.
- PM-ABHIM aligns with this framework to enhance India’s global health resilience.
- Alignment with SDGs
- Directly supports Sustainable Development Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-being).
- Contributes to targets on ending communicable diseases, achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC), and ensuring access to affordable medicines and vaccines by 2030.
- Significance
- Strengthens India’s pandemic preparedness and emergency response capacity.
- Establishes a decentralised and technology-driven health system.
- Enhances surveillance, diagnostics, and tertiary care capacity across rural and urban regions.
- Promotes a research-oriented and inclusive health ecosystem in line with Viksit Bharat 2047 vision.
- Conclusion
- Four years post-launch, PM-ABHIM has become a cornerstone of India’s health infrastructure transformation.
- Through a multi-level approach—combining infrastructure, research, digitalisation, and surveillance—it ensures India’s preparedness for future pandemics while advancing towards Universal Health Coverage and SDG-3 targets.
Static Information
- Launched by: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- Launch Year: 2021
- Duration: 2021–26
- Total Outlay: ₹64,180 crore
- Policy Foundation: National Health Policy (2017)
- Linked Schemes: NHM, AB-PMJAY, ABDM
- Approach: One Health, Universal Health Coverage
- Global Link: WHO Pandemic Agreement (2025), International Health Regulations (2024)

Updated - 24 OCT 2025 3:39 PM | PIB