Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana Completes Nine Years
IN NEWS: Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana Completes Nine Years
ANALYSIS
1. Context
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) marks its nine-year completion on 18 February 2025.
- Launched in 2016, aimed at protecting farmers from crop losses arising due to natural calamities.
- PMFBY continues to act as a comprehensive income-stabilisation mechanism for India’s agricultural sector.
2. Cabinet Approval for Continuation
- In January 2025, the Union Cabinetapproved the continuation of:
- PMFBY
- Restructured Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme (RWBCIS)
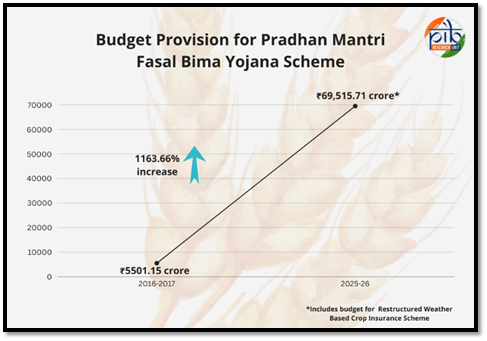
- Approved period: Up to 2025–26
- Total financial allocation: ₹69,515.71 crore.
3. PMFBY vs RWBCIS
- PMFBY:
- Based on actual yield assessment.
- Uses CCEs (Crop Cutting Experiments) for estimating losses.
- RWBCIS:
- Weather index-based insurance.
- Compensation is calculated on the basis of weather triggers such as rainfall, temperature, humidity etc.
- Main difference lies in methodology of admissible claim calculation.
4. Technological Interventions
- Advanced Monitoring Tools:
- Satellite imagery, drones, UAVs, remote sensing for:
- Crop area estimation
- Yield disputes
- Loss assessment
- Planned CCE execution
- Clustering of districts
- Satellite imagery, drones, UAVs, remote sensing for:
- Digital Integration:
- Yield data captured via CCE-Agri App, uploaded to the National Crop Insurance Portal (NCIP).
- State land records integrated with NCIP for enhanced transparency.
- YES-TECH (from Kharif 2023):
- Technology-based yield estimation system.
- Blends manual and technology-driven yield data.
- Aims to reduce reliance on manual CCEs and improve accuracy and timeliness of claim settlement.
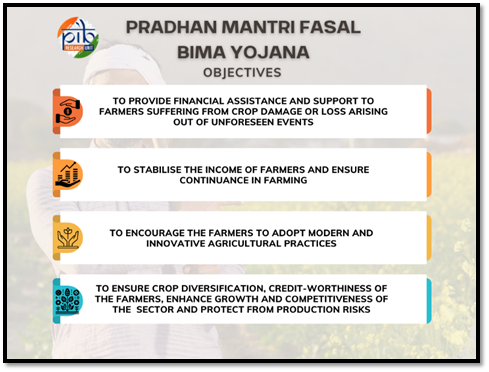
5. Key Benefits of PMFBY
- Affordable Premium Structure:
- Kharif: 2% of sum insured
- Rabi: 1.5%
- Annual commercial/horticultural crops: 5%
- Remaining premium borne by the Government.
- Comprehensive Risk Coverage:
Covers:- Natural calamities (drought, floods, cyclones)
- Pest and disease attacks
- Post-harvest losses (up to 14 days for crops kept in “cut and spread” condition)
- Localised calamities (hailstorm, landslide, inundation)
- Prevented sowing (up to 25% of sum insured)
- Timely Compensation:
- Target: Settlement of claims within two months of harvest.
- Technology-Driven Implementation:
- Ensures accuracy, accountability and transparency.
6. Strengthening PMFBY
- Multiple reforms since 2016 have improved transparency and timeliness.
- 2023–24:
- Highest-ever area and farmer coverage.
- Now the largest crop insurance scheme globally based on farmer applications.
- Several States have waived farmers’ premium share—reducing burden on farmers.
7. Eligibility and Participation
- Scheme is voluntary for all farmers.
- Non-loanee farmers now form 55% of total enrolments (2023–24), indicating high voluntary acceptance.
NECESSARY STATIC PART
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
- Objective: Provide financial support for losses to standing crops due to non-preventable natural risks.
- Implemented by: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare.
- Introduced: 2016.
- Crop Cutting Experiments (CCEs)
- Conducted to estimate actual yield of crops in notified insurance units.
- Required for crop insurance loss computation.
- National Crop Insurance Portal (NCIP)
- Digital platform for enrolment, claim processing, CCE data upload and transparency.
- Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme (WBCIS / RWBCIS)
- Uses objective weather parameters for estimating crop losses.

Updated - 17 Feb 2025 ; 07:25 PM | News Source: PIB (https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=2104175)