Sagarmanthan 2024 – India’s Maritime Vision

Sagarmanthan 2024 – India’s Maritime Vision
Context:
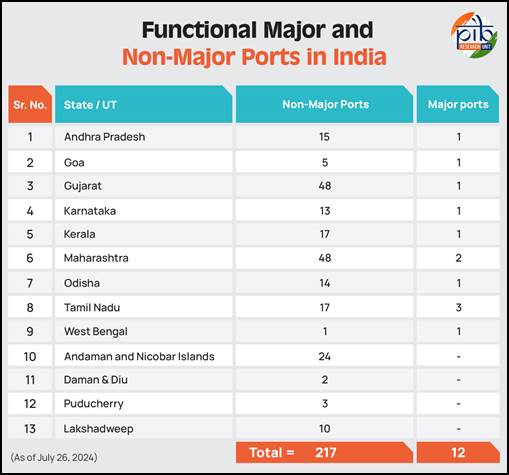
India, with a 7,500 km coastline, 12 major ports, and over 200 minor/intermediate ports, is strategically located on key global shipping lanes. Handling 95% of the country’s trade by volume and 70% by value, the maritime sector is a critical driver of commerce, connectivity, and international engagement. India also ranks 16th globally in maritime presence, operates 1,530 ships, and is the third-largest ship recycling nation by tonnage.
Key Highlights from Sagarmanthan 2024:
- Event Overview: First edition of Sagarmanthan: The Great Oceans Dialogue held on 18–19 Nov 2024 in New Delhi. Organized by MoPSW in collaboration with ORF, the event aimed to bring together policymakers, business leaders, and maritime experts to discuss sustainable maritime growth, blue economy, and global supply chains.
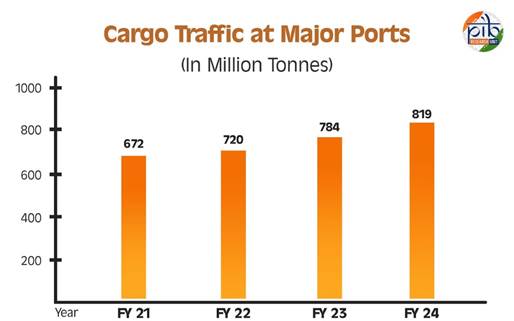
- Cargo Handling & Growth: Indian ports handled 819.22 MT cargo in FY24, a 4.45% increase from the previous year. Major ports’ annual handling capacity grew from 871.52 MT in 2014–15 to 1,629.86 MT in 2023–24 (87% increase). Paradip Port became India’s largest major port by volume (145.38 MT).
- Government Initiatives:
- Sagarmala Programme: Focus on port modernization, connectivity, coastal community development, and port-led industrialization. 130 projects sanctioned with ₹3,714 crore allocation (as of July 2024).
- Maritime India Vision 2030 (MIV 2030): 150+ initiatives covering ports, shipyards, inland waterways, and trade promotion.
- Green Tug Transition Program (GTTP): Phasing out conventional fuel-based tugs, target 2040 for full green fleet.
- Shipbuilding Financial Assistance Policy (SBFAP): ₹337 crore support; 313 vessel orders worth ₹10,500 crore.
- New Port & Fleet Expansion: Vadhavan port (Maharashtra) approved at ₹76,220 crore; plan to add 1,000 ships in the next decade to reduce foreign freight costs by 1/3 by 2047.
- Sustainability & Smart Ports: Initiatives include smart ports, green hydrogen hubs, digitization, and coastal economic development. Container turnaround time reduced to 22.57 hours, exceeding global benchmarks.
Strategic Implications:
- Economic: Boosts exports, reduces logistics costs, and strengthens India’s position as a global trade hub.
- Environmental: Green shipping and eco-friendly port operations align with climate goals and sustainable development.
- Geopolitical: Enhanced maritime infrastructure and engagement reinforce India’s influence in the Indo-Pacific region and global maritime governance.
- Social: Coastal community development ensures livelihood security for fisherfolk and port-dependent populations.
Conclusion:
Sagarmanthan 2024 signals India’s integrated maritime vision combining trade expansion, sustainability, and strategic governance. Through schemes like Sagarmala, MIV 2030, and GTTP, India is positioning itself as a future-ready maritime power, ensuring economic growth, environmental stewardship, and global influence.

Updated - 19 NOV 2024 4:47 PM | PIB