Towards Atmanirbharta in Agriculture
IN NEWS — Towards Atmanirbharta in Agriculture
ANALYSIS
- Context:
India has made remarkable progress towards Atmanirbharta (self-reliance) in agriculture over the last decade, focusing on empowering farmers, enhancing domestic production, and reducing import dependency. The approach combines policy reforms, financial inclusion, digital empowerment, and infrastructure creation, placing farmers at the center of India’s development vision for Amrit Kaal. - Budgetary Support:
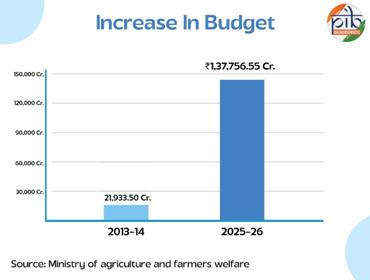
- Budget allocation for the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare increased from ₹21,933.50 crore (2013–14) to ₹1,37,756.55 crore (2025–26).
- Reflects a sixfold rise, showcasing the government’s commitment to the agriculture sector.
- Food Grain Production:
- Increased from 246.42 million tonnes (2013–14) to 353.96 million tonnes (2024–25) as per the third advanced estimates.
- MSP Reforms:
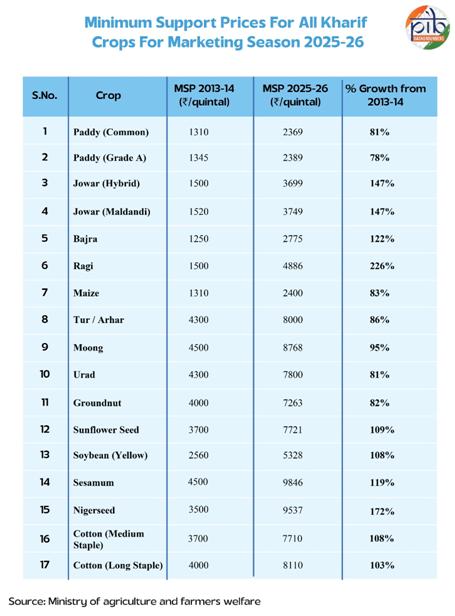
- Since 2018–19, MSP for all mandated crops ensures a minimum 50% return over the all-India weighted average cost of production.
- MSP (2025–26): Paddy (₹2369/qtl) and Wheat (₹2425/qtl), up from ₹1940 and ₹1975 in 2021–22 respectively.
- Key Farmer-Centric Schemes:
- PM-KISAN (2019): ₹6000 annual income support; ₹3.90 lakh crore disbursed via 20 installments till Aug 2025.
- PM-KMY: 24.88 lakh farmers enrolled as of July 2025.
- PMFBY: 78.41 crore applications insured; ₹1.83 lakh crore claims paid; non-loanee coverage rose sharply to 522 lakh (2024–25).
- PMKSY: ₹93,000+ crore allocated (2021–26) for irrigation; 112 projects implemented.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC): ₹10 lakh crore credit extended to 7.71 crore farmers; limit raised from ₹3 to ₹5 lakh (2025–26).
- Soil Health Card Scheme: 25.17 crore cards issued; 8,272 soil labs established.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Development:
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF): ₹66,310 crore sanctioned for 1,13,419 projects, mobilizing ₹1,07,502 crore investments.
- Projects include processing units, cold storage, warehouses, grading and sorting facilities, and custom hiring centers.
- Digital and Institutional Innovations:
- e-NAM: 1,522 mandis integrated; ₹4.39 lakh crore trade value with over 1.79 crore farmers and 4,518 FPOs.
- Kisan Samriddhi Kendras: 1.8 lakh operational centers (as of May 2025).
- National Mission on Natural Farming (2024): Promotes chemical-free farming; aims to train 1 crore farmers with ₹2481 crore outlay.
- Sustainable & Organic Farming:
- PKVY: ₹31,500 per hectare support for organic farming; 14.99 lakh hectares covered; 52,289 clusters formed, benefiting 25.30 lakh farmers.
- Millets (Shree Anna): Production rose to 18.02 million tonnes (2024–25); India contributes 38.4% of global millet output.
- Agri-Entrepreneurship & Women Empowerment:
- Namo Drone Didi (2023–26): 15,000 drones to Women SHGs; ₹1261 crore outlay; 80% financial assistance up to ₹8 lakh per drone.
- AgriSURE Fund: 1,943 agri-startups supported under RKVY (2019–25); over 7,000 startups registered in agriculture and allied sectors.
- Agro-Industrial Development:
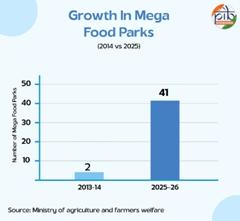
- Mega Food Parks: Expanded from 2 (2014) to 41 (2025), with 24 operational and 17 under implementation, enhancing farm-to-market linkages.
STATIC PART (RELEVANT FACTS)
- Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare
- Flagship Missions: PM-KISAN, PMFBY, PMKSY, AIF, PKVY, NMNF
- Vision: Self-reliant, technology-driven, and sustainable agriculture sector aligned with Viksit Bharat 2047.
- Focus Areas: Income support, irrigation, risk coverage, infrastructure, sustainability, innovation, and women empowerment.
Updated – 15 Aug 2025 ; 2:39 PM | PIBSource: PIB – Click Here