University of Hyderabad Converts Geranium Waste into Low-Cost Biochar
IN NEWS: University of Hyderabad Converts Geranium Waste into Low-Cost Biochar
Why Geranium Biochar is in News?
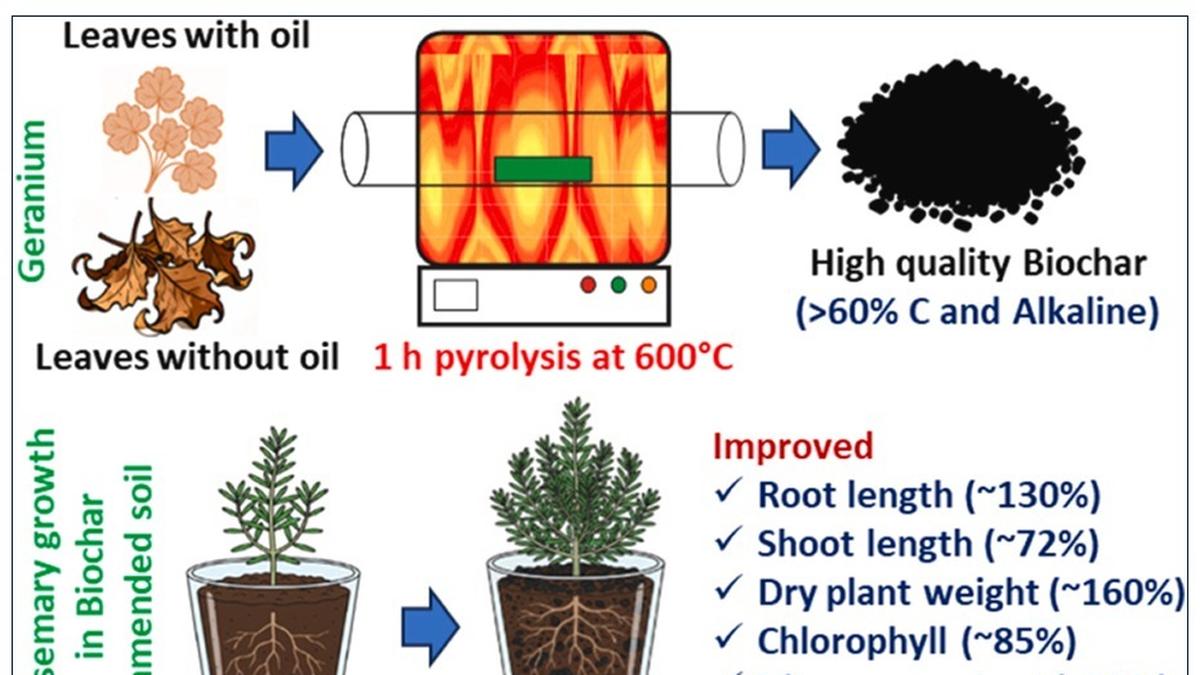
The University of Hyderabad (UoH) has successfully developed a method to convert Geranium waste generated during oil extraction into low-cost biochar, which has been proven to enhance soil fertility and plant growth. The process is energy-efficient and economical, making it a promising solution for sustainable agriculture.
What is Geranium Biochar?
Geranium biochar is a carbon-rich product produced from Geranium leaf waste, including pre- and post-oil extraction residues. It functions as a soil amendment and carbon-storage material, contributing to improved plant growth and soil health.
Objectives
- To upcycle Geranium plant residue into a value-added agricultural product.
- To promote sustainable waste utilization and reduce environmental load.
- To design a cost-effective and energy-efficient biochar production method.
- To explore soil enhancement solutions for improving crop yield.
- To support circular bioeconomy practices in agriculture.
Role and Functions of Geranium Biochar
- Improves Soil Quality – enhances nutrient availability and soil structure.
- Carbon Sequestration – stores carbon in stable form, reducing emissions.
- Plant Growth Enhancer – demonstrated effective growth support in Rosemary crops.
- Waste Utilization – transforms discarded Geranium biomass into productive resource.
- Cost Reduction for Farmers – low production cost increases accessibility.
Research Details
- Research conducted by University of Hyderabad involving Life Sciences and Engineering Sciences & Technology departments.
- Project led by scientists Appa Rao Podile and V.V.S.S. Srikanth.
- Findings published in the Biomass and Bioenergy journal.
- Biochar produced contains ~65% carbon along with essential minerals.
- Trial application on soil demonstrated positive growth response in Rosemary plants.
Significance
- Helps reduce agricultural waste disposal issues.
- Supports soil rejuvenation in degraded farmlands.
- Contributes to climate mitigation through carbon storage.
- Encourages scaling of biochar-based soil management in India.
- Useful across multiple regions cultivating aromatic crops for oils.
Way Forward
- Large-scale pilot projects needed to integrate Geranium biochar in farming systems.
- Promote farmer awareness and field demonstrations for adoption.
- Encourage research on multi-crop applicability and soil type-specific performance.
- Government support through subsidy and policy incentives for biochar technologies.
- Explore commercial production linking agro-industries, farmers, and research institutions.
Updated - 25 November 2025 ; 5:30 PM | News Source: The Hindu