World Bank Ranks India 4th Among the World’s Most Equal Societies
World Bank Ranks India 4th Among the World’s Most Equal Societies – Analysis
1. Key Findings
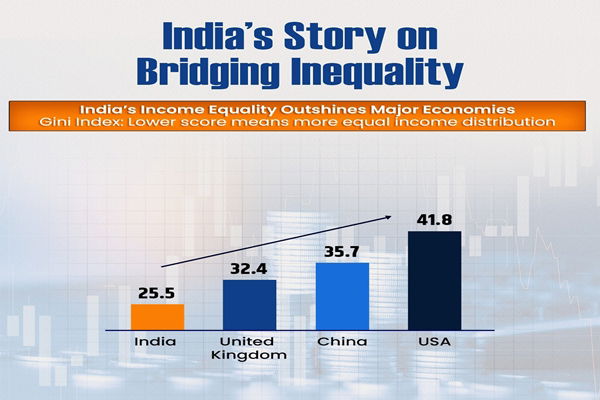
- India’s Gini Index (2022): 25.5
- Rank: 4th most equal society in the world.
- Countries ahead of India: Slovak Republic (24.1), Slovenia (24.3), Belarus (24.4).
- Data Coverage: World Bank released data for 167 countries.
- Category: India falls under “Moderately Low Inequality” (Gini between 25–30).
- Trend: Gini Index declined from 28.8 (2011) → 25.5 (2022), showing a reduction in inequality.
2. What the Gini Index Measures
- Meaning:
- A statistical measure of income or wealth inequality.
- Scale: 0 = perfect equality; 100 = perfect inequality.
- Lower score → more equitable society.
- Interpretation for India:
- India’s low Gini score (25.5) indicates that income and consumption are more evenly distributed compared to most economies.
3. Global Comparison
| Country | Gini Index | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Slovak Republic | 24.1 | Most equal |
| Slovenia | 24.3 | — |
| Belarus | 24.4 | — |
| India | 25.5 | 4th most equal |
| China | 35.7 | High inequality |
| United States | 41.8 | Very high inequality |
🔹 India outperforms 167 other nations, including major economies like China, USA, Brazil, South Africa, etc.
4. India’s Progress Over the Years
- 2011: Gini Index 28.8
- 2022: Gini Index 25.5
➡️ Indicates a consistent decline in inequality, showing inclusive economic growth and effective redistribution policies.
5. Economic Implications
- Positive Signs:
- Strong performance in rural inclusion, direct benefit transfers, and social welfare schemes.
- Expanding middle class and growing formalization of the economy.
- Challenges Ahead:
- Persistent regional disparities (urban vs. rural, state-level differences).
- Wealth concentration among top income groups.
- The need to sustain equity while maintaining high growth
Updated - July 5, 2025 9:22 PM | News On Air