World Health Day 2025: Strengthening Indian Healthcare for a Resilient Future

IN NEWS – World Health Day 2025: Strengthening Indian Healthcare for a Resilient Future
Analysis
- Context and Theme:
- World Health Day is observed annually on 7 April, established by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1950 to raise awareness on global health priorities.
- The 2025 theme – “Healthy Beginnings, Hopeful Futures” focuses on maternal and newborn health, advocating for the elimination of preventable deaths and the long-term well-being of women and children.
- India’s Commitment to Public Health:
- The Government of India continues to emphasize equitable, accessible, and quality healthcare, aligning with the WHO’s vision through initiatives led by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
- Flagship schemes such as Ayushman Bharat, National Health Mission (NHM), and Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) have driven significant improvements in healthcare access and infrastructure.
- Maternal and Child Health Achievements:
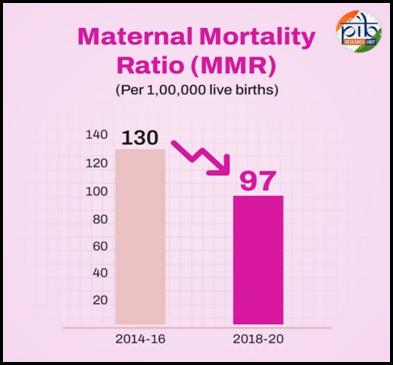
- Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) dropped from 130 (2014–16) to 97 (2018–20) — a 33-point reduction, marking an 83% decline since 1990, compared to the global 42%.
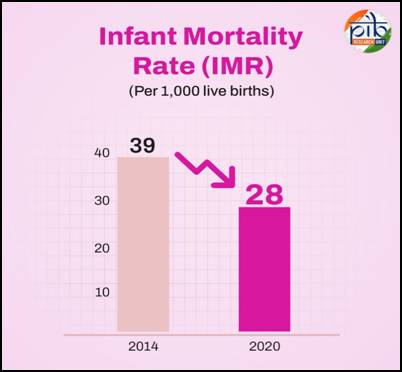
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) reduced from 39 (2014) to 28 (2020) per 1,000 live births.
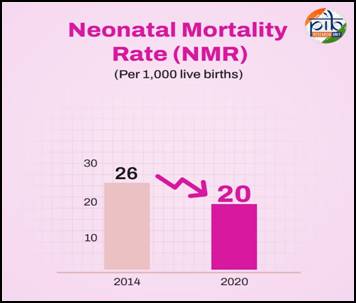
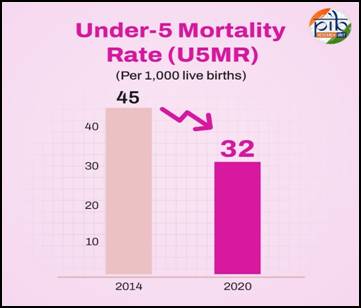
- Neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR) declined from 26 to 20, and Under-5 Mortality Rate (U5MR) from 45 to 32 per 1,000 live births (2014–2020).
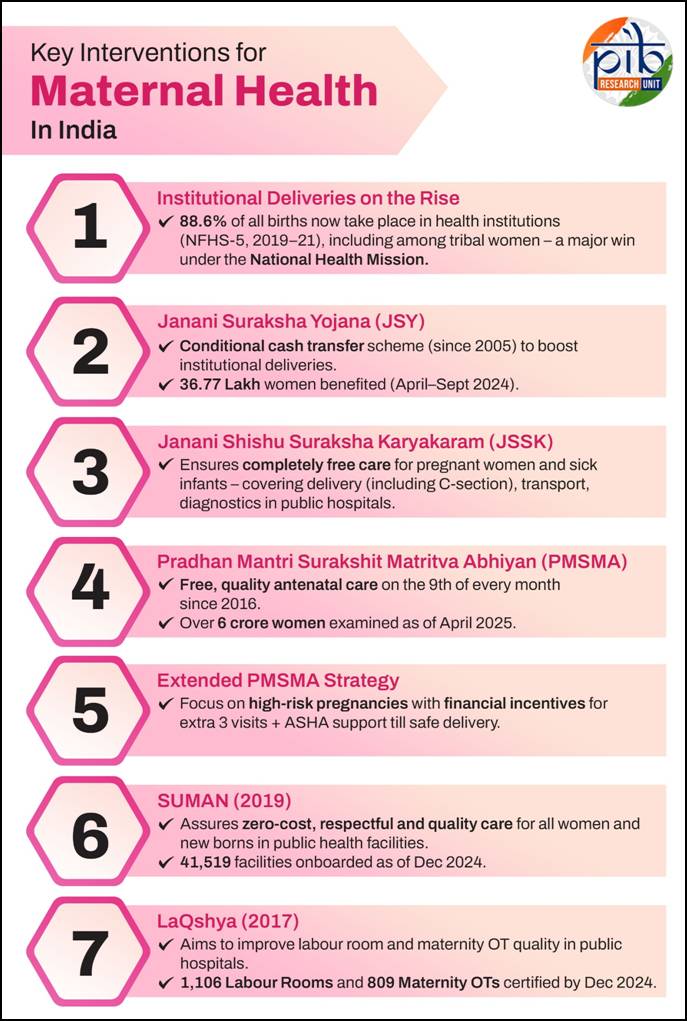
- Maternal Health Interventions:
- Maternal Death Surveillance and Response (MDSR) to identify causes and improve obstetric care.
- Mother and Child Protection (MCP) Card and Safe Motherhood Booklet to educate women on nutrition, institutional delivery, and government benefits.
- Reproductive and Child Health (RCH) Portal for digital tracking of antenatal and postnatal care.
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat (AMB) under POSHAN Abhiyaan to reduce anaemia among adolescents and pregnant women.
- Birth Waiting Homes (BWH) and Village Health, Sanitation & Nutrition Day (VHSND) to improve institutional deliveries and rural healthcare outreach.
- Expansion of Primary Healthcare Access:
- 1.76 lakh Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (Health & Wellness Centres) operational as of April 2025.
- Over 107 crore screenings for hypertension and 94 crore for diabetes conducted.
- 17,000+ health facilities certified under the National Quality Assurance Standards (NQAS) for patient-centric healthcare.
- Digital Health Innovations:
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM):
- 76 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) created.
- 5.95 lakh healthcare professionals and 3.86 lakh health facilities verified.
- U-WIN Platform: For tracking immunization; 7.9 crore beneficiaries registered and 29.2 crore vaccine doses administered.
- eSanjeevani Telemedicine: Over 36 crore teleconsultations provided since 2020 with 2.3 lakh providers onboarded.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM):
- Disease Elimination and Control:
- Malaria: 69% drop in cases and 68% fall in deaths (2017–2023); India exited WHO’s High Burden to High Impact group in 2024.
- Trachoma: Eliminated as a public health problem (2024).
- Measles and Rubella: Over 50 districts reported zero cases (2024).
- Tuberculosis: Incidence declined by 17.7% (2015–2023); deaths reduced from 28 to 22 per lakh; 83% fall in missing TB cases.
- Kala-azar: Eliminated nationwide by October 2024, meeting WHO target.
- Health Insurance and Affordability:
- Ayushman Bharat–PMJAY:
- 55 crore beneficiaries covered with ₹5 lakh per family insurance.
- 40 crore Ayushman Cards issued; 8.5 crore hospital admissions recorded.
- 31,846 hospitals empanelled across India (17,434 public + 14,412 private).
- Coverage extended to ASHA and Anganwadi workers.
- Ayushman Bharat–PMJAY:
- Mental Health and Well-Being:
- Tele-MANAS: Operational in 53 cells across 36 States/UTs, offering 24x7 multilingual support.
- Over 20 lakh calls handled; ₹230 crore allocated under the National Tele-Mental Health Programme.
- 440+ Rehabilitation and Halfway Homes established under the Manoashraya Dashboard.
- Conclusion – Towards a Resilient Health Future:
- India’s healthcare transformation reflects a multi-tiered approach combining preventive, curative, and digital health measures.
- Through Ayushman Bharat, NHM, Tele-MANAS, and disease elimination drives, India is advancing toward Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and resilient public health systems.
Static / Background Information
- World Health Day: Established in 1950 by WHO; observed every 7 April to raise global health awareness.
- Ayushman Bharat Scheme (2018): Comprises Health & Wellness Centres (HWCs) and PM-JAY for primary and secondary healthcare coverage.
- National Health Mission (NHM): Launched in 2013 to strengthen health infrastructure and service delivery.
- WHO’s Sustainable Development Goal (SDG 3): Ensures healthy lives and promotes well-being for all at all ages.



Updated – 06 Apr 2025 ; 7:27 PM | PIBNews Source:PIB Press Release