World Milk Day 2025: India’s Dairy Growth, Livestock Strength & Schemes Driving the Sector

IN NEWS — World Milk Day 2025: India’s Dairy Growth, Livestock Strength & Schemes Driving the Sector
ANALYSIS
1. Significance of World Milk Day 2025
- Celebrated annually on 1 June, declared by FAO in 2001 to highlight milk's contribution to nutrition, economy, and livelihoods.
- Theme for 2025: “Let’s Celebrate the Power of Dairy.”
- Recognises milk as:
- A source of nutrition and immunity
- A livelihood base for millions of farmers
- A contributor to rural economic stability
- A sustainable food system element when managed responsibly
2. India’s Transformation from Milk Deficit to Dairy Powerhouse
- At Independence, milk production was less than 21 million tonnes, and per capita availability was 124 g/day (1950–51).
- Structural shift came with the creation of NDDB (1965) under Dr Verghese Kurien.
- Operation Flood (1970–1996)established:
- 73,000+ dairy cooperatives
- Supply of quality milk to 700 towns
- Self-sufficiency and export capability
3. India’s Present Dairy Scenario
- India is the world’s largest milk producer since 1998, contributing 25% of global milk.
- Per capita availability increased to 471 g/day (2023–24) vs global 322 g/day.
- Milk production rose 63.56% from 146.3 MT (2014–15) to 239.2 MT (2023–24); CAGR 5.7%.
- State performance:
- Uttar Pradesh: Highest contributor at 16.21%.
- West Bengal: Fastest growth at 9.76% over previous year.
4. Livestock Base and Dairy Workforce
- India has 303.76 million bovines, 74.26 million goats, and a total livestock population of 536.76 million.
- Dairy cooperatives include:
- 22 Federations/Apex Bodies
- 240 district milk unions
- 28 marketing dairies
- 24 Milk Producer Organisations
- Presence in 2.3 lakh villages, with 18 million dairy farmers.
- Women’s participation significant at 35%, with 48,000 women dairy cooperatives.
- Dairy contributes 5% to national economy and provides direct livelihood to over 8 crore farmers.
5. Key Schemes Supporting India’s Dairy Sector
A. Rashtriya Gokul Mission (2014)
- Aim: Development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds.
- Allocation: ₹3400 crore (2021–26).
- Achievements so far:
- 8.87 crore animals covered
- 13.43 crore Artificial Inseminations performed
- 5.42 crore farmers benefited
- Target: Raise AI coverage from 30% to 70%.
B. National Programme for Dairy Development (NPDD)
- Launched 2014, restructured 2021 (2021–26).
- Focus: Infrastructure creation for procurement, processing, marketing of quality milk.
- Implemented through State Cooperative Dairy Federations.
C. Livestock Health & Disease Control Programme (LHDCP)
- Revised version approved in March 2025, with outlay ₹3880 crore (2024–26).
- Components:
- NADCP
- LH&DC (CADCP, ESVHD-MVU, ASCAD)
- Pashu Aushadhi (generic veterinary medicines; ₹75 crore allocation)
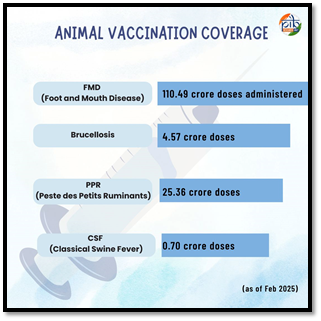
- GOI funds vaccination for FMD, Brucellosis, PPR, CSF across all States/UTs.
D. National Livestock Mission (NLM)
- Launched 2014–15, realigned 2021–22.
- Sub-missions:
- Breed Development
- Feed and Fodder Development
- Extension & Innovation
- Aims to enhance productivity, entrepreneurship and meet domestic nutritional demand.
E. Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF)
- Started June 2020 under Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Supports:
- Dairy and meat processing infrastructure
- Animal feed plants
- Breed improvement technologies
F. Kisan Credit Cards (KCC) for Dairy Farmers
- Introduced for dairy and livestock farmers from 2019.
- Improves access to affordable institutional credit.
6. Overall Assessment
- India’s dairy sector has evolved into the largest agricultural commodity segment.
- Strong cooperative systems and women’s participation underpin inclusive growth.
- Technological interventions, disease control, breed improvement and infrastructure development remain key to sustaining high growth.
- Policy focus remains on increasing productivity, improving farmer incomes, and expanding value-added dairy products.
NECESSARY STATIC PART
- World Milk Day established by FAO in 2001.
- NDDB is headquartered in Anand, Gujarat.
- Operation Flood is known as the White Revolution.
- FMD and Brucellosis are major livestock diseases targeted for eradication.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) was originally launched in 1998 for farmers, later extended to dairy farmers in 2019.


Updated – 31 May 2025 ; 08:28 PM | PIB | News Source: PIB (https://www.pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?id=154532&NoteId=154532&ModuleId=3)